Your current location:
- Home>
- Achievements>
- Research Papers
Ultrathin Oxide Layer-Wrapped Noble Metal Nanoparticles via Colloidal Electrostatic Self-Assembly for Efficient and Reusable Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering Substrates
Author: Haoming Bao, Hongwen Zhang, Le Zhou, Guangqiang Liu, Yue Li , and Weiping Cai
Periodical: Langmuir
Page:
Full text link: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b02610
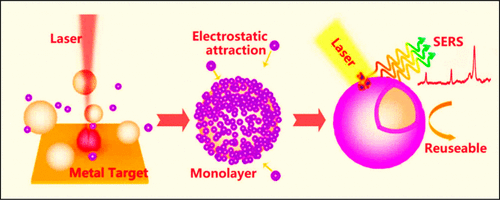
Controllable and flexible fabrication of ultrathin and uniform oxide layer-wrapped noble metal nanoparticles (NPs) has been expected. Here a new strategy is presented for them based on colloidal electrostatic attraction and self-assembly on the metal NPs via one-step laser ablation of noble metal targets in the hydrolysis-induced hydroxide sol solutions at room temperature. The Au NPs, with several tens of nanometers in size, are taken as core part and TiO2 as shell-layer to demonstrate the validity of the presented strategy. It has been shown that the TiO2 shell-wrapped Au NPs are obtained after laser ablation of Au target in the hydrolysis-induced Ti(OH)4sol solution. The Au NPs are about 35 nm in mean size, and the TiO2 shell layers are amorphous in structure and about 2.5 nm in thickness. The shell thickness is nearly independent of the Au NPs¡¯ size. Further experiments have shown that the thickness and crystallinity of the shell-layer can be tuned and controlled via changing the temperature or pH value of the Ti(OH)4 sol solution or prolonging the laser ablation duration. The formation of the TiO2 shell-wrapped Au NPs is attributed to attachment and self-assembly of Ti(OH)4 colloids on the laser-induced Au NPs due to the electrostatic attraction between them. Importantly, the presented strategy is universal and suitable for fabrication of many other ultrathin oxide-wrapped noble metal NPs. A series of oxide shell-wrapped noble metal NPs have been successfully fabricated, such as Au@oxides (Fe2O3, Al2O3, CuO, and ZnO) as well as Pt@TiO2 and Pd@TiO2, etc. Further, compared with the pure gold NPs-built film, the TiO2-wrapped Au NPs-built film has exhibited much stronger surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) performance to the anions NO3¨C, which weakly interact with noble metals, and the good reusability for the SERS-based detection of 4-nitrophenol, which could be photodegraded by xenon lamp irradiation. This work provides a flexible and universal route to the ultrathin and uniform oxide layer-wrapped noble metal NPs.
Periodical: Langmuir
Page:
Full text link: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b02610

Controllable and flexible fabrication of ultrathin and uniform oxide layer-wrapped noble metal nanoparticles (NPs) has been expected. Here a new strategy is presented for them based on colloidal electrostatic attraction and self-assembly on the metal NPs via one-step laser ablation of noble metal targets in the hydrolysis-induced hydroxide sol solutions at room temperature. The Au NPs, with several tens of nanometers in size, are taken as core part and TiO2 as shell-layer to demonstrate the validity of the presented strategy. It has been shown that the TiO2 shell-wrapped Au NPs are obtained after laser ablation of Au target in the hydrolysis-induced Ti(OH)4sol solution. The Au NPs are about 35 nm in mean size, and the TiO2 shell layers are amorphous in structure and about 2.5 nm in thickness. The shell thickness is nearly independent of the Au NPs¡¯ size. Further experiments have shown that the thickness and crystallinity of the shell-layer can be tuned and controlled via changing the temperature or pH value of the Ti(OH)4 sol solution or prolonging the laser ablation duration. The formation of the TiO2 shell-wrapped Au NPs is attributed to attachment and self-assembly of Ti(OH)4 colloids on the laser-induced Au NPs due to the electrostatic attraction between them. Importantly, the presented strategy is universal and suitable for fabrication of many other ultrathin oxide-wrapped noble metal NPs. A series of oxide shell-wrapped noble metal NPs have been successfully fabricated, such as Au@oxides (Fe2O3, Al2O3, CuO, and ZnO) as well as Pt@TiO2 and Pd@TiO2, etc. Further, compared with the pure gold NPs-built film, the TiO2-wrapped Au NPs-built film has exhibited much stronger surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) performance to the anions NO3¨C, which weakly interact with noble metals, and the good reusability for the SERS-based detection of 4-nitrophenol, which could be photodegraded by xenon lamp irradiation. This work provides a flexible and universal route to the ultrathin and uniform oxide layer-wrapped noble metal NPs.
