Your current location:
- Home>
- Achievements>
- Research Papers
Ultrasonic Emulsification Preparation of Metallic Rubidium Sol and Its Ignition Performance
Author: Guo Yujing£»Bao Haoming£»Fu Hao£»Zhang Hongwen£»Li Wenhong£»Cai Weiping
Periodical: ACTA METALLURGICA SINICA
Page: ¾í58 ÆÚ6 Ò³792-798
Full text link: https://www.ams.org.cn/CN/10.11900/0412.1961.2021.00001
Periodical: ACTA METALLURGICA SINICA
Page: ¾í58 ÆÚ6 Ò³792-798
Full text link: https://www.ams.org.cn/CN/10.11900/0412.1961.2021.00001

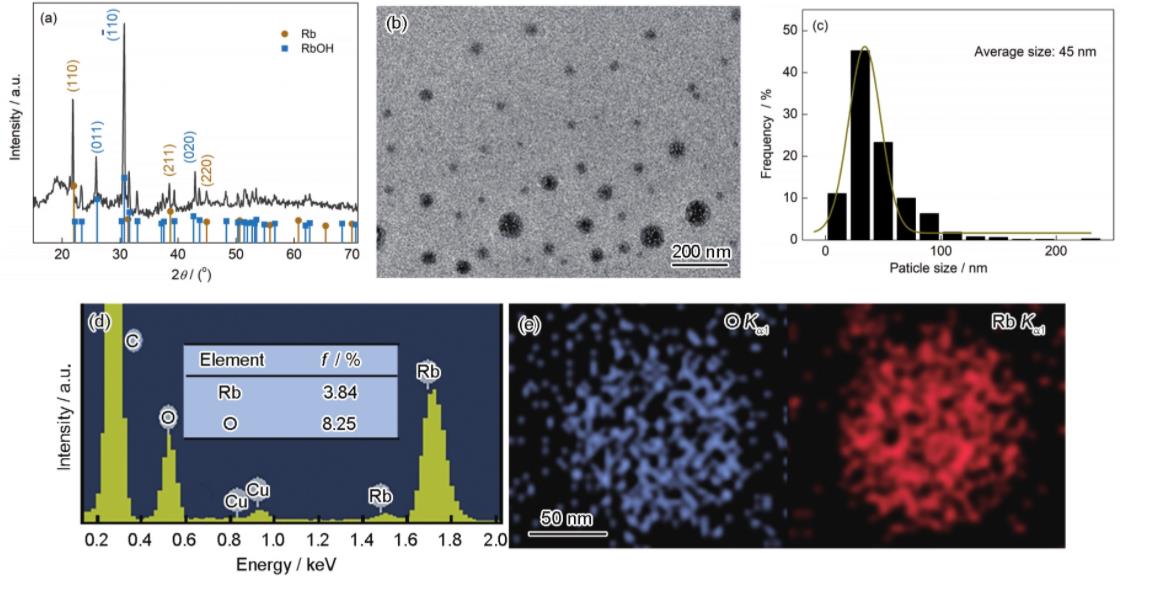
Metallic rubidium (Rb) has great potential in various fields, such as energy, catalysis, and medical treatment. Fragmenting bulk Rb to the nanoscale is essential for its efficient application in these fields. However, as an alkali metal with a high chemical activity, Rb reacts violently with trace water, oxygen, and others; thus, preparing nanosized Rb is challenging. This study proposes a sample solid-liquid transformation and ultrasonic dispersion method to prepare Rb nanoparticles (NPs) utilizing Rb.. s low melting point. This method uses the ultrasonic emulsification of liquid Rb in a specific liquid (toluene) to form a colloidal Rb solution. Typically prepared Rb NPs are nearly spherical with an average size of approximately 45 nm. Further, the average size increases with a decrease in ultrasonic power. When the ultrasonic power falls to 320 and 240 W, the average NP size rises to 55 and 70 nm, respectively, demonstrating good controllability of the proposed method. Further experiments demonstrated that Rb NPs can ignite toluene at relatively low temperatures (say 120 degrees C) within 1 s. When the temperature is up to 250 degrees C, toluene can be ignited in 0.25 s. This study not only provides a new method for synthesizing Rb NPs but also offers new opportunities for novel energy-containing materials and ignition devices.
