Your current location:
- Home>
- Achievements>
- Research Papers
Trace detection of cyanide based on SERS effect of Ag nanoplate-built hollow microsphere arrays
Author: Guangqiang Liu, Weiping Cai, Lingce Kong, Guotao Duan, Yue Li, Jingjing Wang, Zhenxing Cheng
Periodical: Journal of Hazardous Materials
Page: 2013, 248-249 (15 March), PP435-441
Full text link: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304389413000447
Periodical: Journal of Hazardous Materials
Page: 2013, 248-249 (15 March), PP435-441
Full text link: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304389413000447

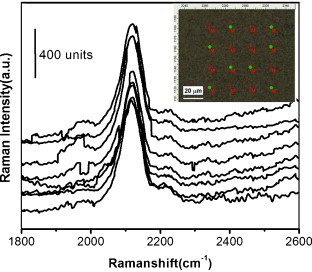
Trace detection of cyanide is studied based on the Ag nanoplate-built hollow microsphere array and its surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) effect. This array was fabricated based on electro-deposition and template method under a low current density. Due to the special structure, such array is a good SERS substrate with high activity and structural stability, and good reproducibility. Such substrate was used for detection of trace amount of kalium cyanide (KCN) in water based on its SERS effect. It has been shown that the detection limit can be down to the level of 0.1 ppb. There exists a good linear double-logarithm relation between the Raman signal and the KCN concentration in water in the range from 0.1 ppb to 1 ppm. In addition, it has been found that the suitable laser power for Raman excitation is crucial to trace detection of KCN molecules. This work is of importance in the practical application in device-design based on the SERS effect of noble metal micro/nano-structured arrays.
