Your current location:
- Home>
- Achievements>
- Research Papers
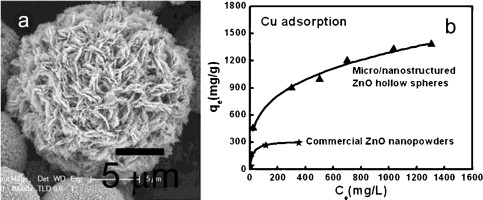
ZnO hollow microspheres with exposed porous nanosheets surface: Structurally enhanced adsorption towards heavy metal ions
Author: Xianbiao Wang Weiping Cai, Shengwen Liua, Guozhong Wanga, Zhikun Wua, Huijun Zhao
Periodical: Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects
Page: 422 (2013) 199¨C 205
Full text link: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0927775713000526
Periodical: Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects
Page: 422 (2013) 199¨C 205
Full text link: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0927775713000526

The micro/nanostructured materials can be used for the high efficient adsorbents owing to their high specific surface area, high surface activity and high stability against aggregation. In this paper, standing porous nanosheet-built ZnO hollow microspheres are produced through a modified hydrothermal route. Such ZnO hollow microspheres with exposed porous nanosheets surface exhibit significantly structurally enhanced adsorption performance for heavy metal cations [Cu(II), Pb(II), Cd(II), and Ni(II), etc.], compared with the commercial ZnO nanopowders, and show much higher adsorption capacities than the surface functionalized activated carbon reported previously. The adsorption isotherms can be described by Langmuir model or Freundlich model, depending on the electronegativity of the heavy metals. This ZnO hollow microspheres with exposed porous nanosheets surface can be used as adsorbent for efficient removal of heavy metal ions from the contaminated water with weak acidity or alkalescence, and easily separated from solution. This study also deepens understanding adsorption behavior of micro/nanostructured ZnO to heavy metal cations.
