Your current location:
- Home>
- Achievements>
- Research Papers
Three-dimensional hierarchically structured PAN@污-AlOOH fiber films based on fiber templated hydrothermal route and their recyclable strong Cr(VI)-removal performance
Author: Yongxing Lin, Weiping Cai, Hui He, Xianbiao Wang and Guozhong Wang
Periodical: RSC Advances
Page: 2012, 2 (5), 1769 - 1773
Full text link: http://pubs.rsc.org/-/content/articlehtml/2012/ra/c2ra00945e
Periodical: RSC Advances
Page: 2012, 2 (5), 1769 - 1773
Full text link: http://pubs.rsc.org/-/content/articlehtml/2012/ra/c2ra00945e

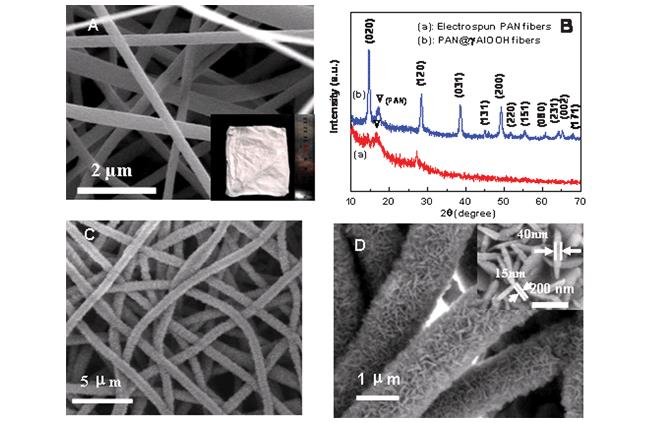
A simple route is presented to fabricate a polymer (polyacrylonitrile, PAN)@污 每AlOOH composite fiber film, with a three-dimensional hierarchical micro/nanostructure, based on electrospun fiber templated hydrothermal strategy. The composite fibers are nest-like in morphology and consist of cross-linked 污每AlOOH nanoplates, with 20 nm每40 nm of thickness, standing nearly vertically on the PAN fibers. The formation of such composite fibers are attributed to the template-induced heterogeneous growth of 污每AlOOH on the PAN fibers in alkaline conditions. Further, such fibers can be converted into the tubular Al2O3 hollow fibers with the nearly unchanged morphology after calcination in air. Importantly, the as-prepared PAN@污每AlOOH composite fibers have shown a much higher adsorption capacity than the normal 污每AlOOH nanopowders, and especially, exhibited very good recycling performance (more than 85% of its original adsorption capacity after 4 cycles), as an adsorbent to remove the heavy metal ions, Cr(VI), from model wastewater. This material could thus serve as an effective recyclable adsorbent with easy separation from solution. Also, it is expected to have other potential applications in the role of a sensitive material or catalyst.
