Temperature regulation growth of Au nanocrystals: from concave trisoctahedron to dendritic structures and their ultrasensitive SERS-based detection of lindane
作者:Xia Zhou, Qian Zhao, Guangqiang Liu, Hongwen Zhang, Yue Li and Weiping Cai
期刊:Journal of Materials Chemistry C
卷(期)页:2017, 5, 10399-10405
全文链接:http://pubs.rsc.org/-/content/articlehtml/2017/tc/c7tc03808a
期刊:Journal of Materials Chemistry C
卷(期)页:2017, 5, 10399-10405
全文链接:http://pubs.rsc.org/-/content/articlehtml/2017/tc/c7tc03808a

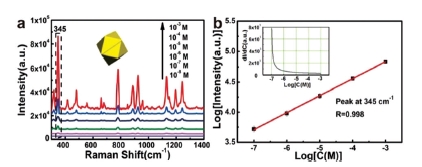
A facile temperature regulation strategy is developed for fabrication of Au concave nanocrystals with specific shapes viaseed-assisted growth at 25 °C or lower. It has been found that the reaction temperature, even with minor changes, can significantly influence the shape of the nanocrystals, which evolves from the concave trisoctahedral to calyptriform, coral and dendritic structures with the decrease of temperature from 25 °C to 5 °C. The size and optical absorbance spectra of the nanocrystals can be determined just by the addition amount of Au seeds. The formation of the Au concave nanocrystals is attributed to the preferential growth of the nuclei in 〈110〉 and 〈111〉 directions, along which the growth rates are of different temperature dependences. Importantly, the concave trisoctahedral and calyptriform Au nanocrystal-built films have exhibited strong surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) activity towards the lindane molecules, with the enhancement factor higher than 107, due to their high density of sharp corners/edges or the tip effect. The Raman peak intensity versus lindane concentration is subject to a linear double logarithmic relation from 30 ppb to 300 ppm, which is attributed to the Freundlich adsorption of lindane molecules on the Au nanocrystals. This work provides not only a simple route for the fabrication of the Au nanocrystals with various specific structures but also efficient SERS substrates for trace detection of organochlorine pesticide residues.
