Metal-organic framework derived nitrogen-doped porous carbon@graphene sandwich-like structured composites as bifunctional electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions
作者:Shengwen Liu , Haimin Zhang, Qian Zhao, Xian Zhang, Rongrong Liu, Xiao Ge, Guozhong Wang, Huijun Zhao, Weiping Cai
期刊:Carbon
卷(期)页: 106 (2016) 74-83
全文链接:http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S000862231630375X
期刊:Carbon
卷(期)页: 106 (2016) 74-83
全文链接:http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S000862231630375X

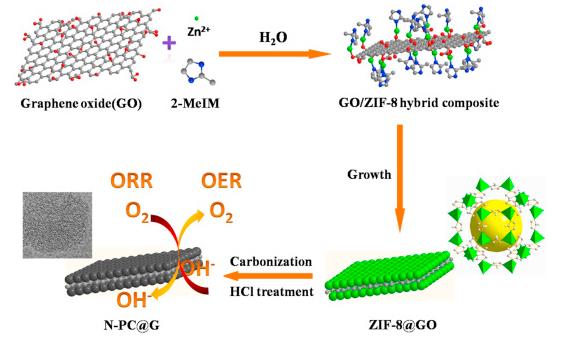
In this work, we have successfully prepared sandwich-like structured N-doped porous carbon@graphene composites (N-PC@G) derived from sandwich-like structured zeolitic imidazolate framework@graphene oxide (ZIF-8@GO). ZIF-8@GO was obtained by in situ controllable growth of ZIF-8 nanocrystals on both surfaces of graphene oxide (GO) sheets with different contents. Experimental results demonstrate that N-PC@G-0.02 (representing GO amount of 0.02 g in reaction precursors) obtained at 900 °C possesses high surface area (1094.3 m2 g−1), bimodal-pore structure (micropores and mesopores) and high graphitization degree, exhibiting great potential as a bifunctional electrocatalyst for both ORR and OER. Compared to commercial Pt/C catalyst, the N-PC@G-0.02 shows superior electrocatalytic activity with onset and half-wave potentials of 1.01 V and 0.80 V (vs. RHE), respectively, better durability and high resistance to methanol crossover effect toward ORR in alkaline media. Also, the metal-free N-PC@G-0.02 also exhibits high electrocatalytic activity of OER, comparable to commercial RuO2 catalyst. The superior ORR and OER performance could be due to a synergistic effect between ZIF-8 derived porous carbon and graphene with regard to structure and composition of N-PC@G-0.02 with high surface area, porous structure, and suitable N doping level and type, boosting the catalytic active sites, mass transport and electron transfer.
