Standing Ag Nanoplate-built Hollow-Sphere Micro/nanostructured Arrays: Controllable Structural Parameters and Structurally Enhanced SERS Performances
作者:Guangqiang Liu, Weiping Cai, Lingce Kong, Guotao Duan, Yue Li, Jingjing Wang, Guomin Zuo, Zhenxing Cheng
期刊:J. Mater. Chem.
卷(期)页: 2012, 22, 3177-3184
全文链接:http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2012/jm/c1jm14296h
期刊:J. Mater. Chem.
卷(期)页: 2012, 22, 3177-3184
全文链接:http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2012/jm/c1jm14296h

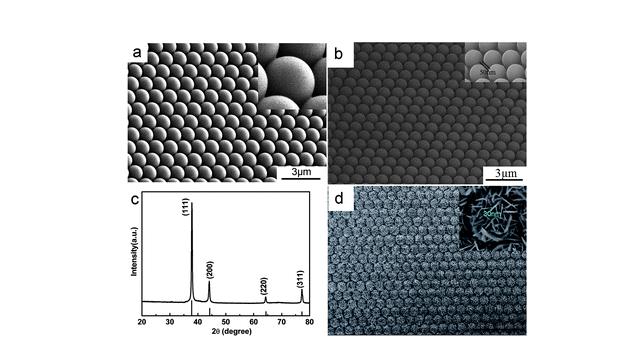
A simple and flexible strategy is presented to fabricate the Ag nanoplate-built hollow microsphere arrays with centimetre-squared scale, based on electrodeposition onto the Au-coated monolayer colloidal crystal template. The array consists of periodically arranged micro-sized hollow spheres, which are built by vertically standing and cross-linking Ag nanoplates. The nanoplates are of single crystal in structure, several hundred nanometres in the planar dimension and about 30 nm in thickness. The number density and size of silver nanoplates can be controlled by the deposition conditions. The formation of nanoplates is mainly attributed to the electrodeposition-induced nanoplates' growth in the initial stage and subsequent electrophoretic deposition-induced oriented connection of Ag nanoparticles, formed in solution, under a low current density. Importantly, such hollow sphere micro-/nano-structured arrays have shown significant surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) effect associated with their geometry, exhibiting strong SERS performances with high stability and good homogeneity. The enhanced factor is higher than 108. The minimum detectable concentration of 4-aminothiophenol molecules can be lower than 10−15 M. Further, such arrays could be re-usable based on an argonplasma cleaning method. This study is of significance, not only in the deep understanding Ag nanoplates' formation andgrowth, but also in device application of micro-/nano-structured arrays based on SERS effect.
